Technologies applied
Our projects have been effectively implemented by flexibly applying the following key elements: Digitization, Automation, Data Analytics, IoT (Internet of Things), Cloud Computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning.
1. Digitization
Digitization is the process of converting information from physical formats (paper documents, images, audio, etc.) into digital formats (digital files). This is the initial and crucial step in a business's digital transformation journey.

Figure 1.1: Illustration of Digitization concept.
Purpose of Digitization
- Efficient storage and preservation of information:
- Reduces physical storage space.
- Enhances security and prevents information loss.
- Facilitates easy search and retrieval of data.
- Creates a foundation for technology applications:
- Digitization is a prerequisite for applying new technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and process automation.
- Enables the creation of new digital products and services, enhancing customer experience.
- Improves operational efficiency:
- Automates manual processes, reducing errors and shortening processing time.
- Enhances connectivity and information sharing among departments.
- Facilitates easy search and retrieval of data.
- Enhances competitiveness:
- Helps businesses adapt quickly to market changes.
- Optimizes operational costs.
- Opens up new business opportunities.
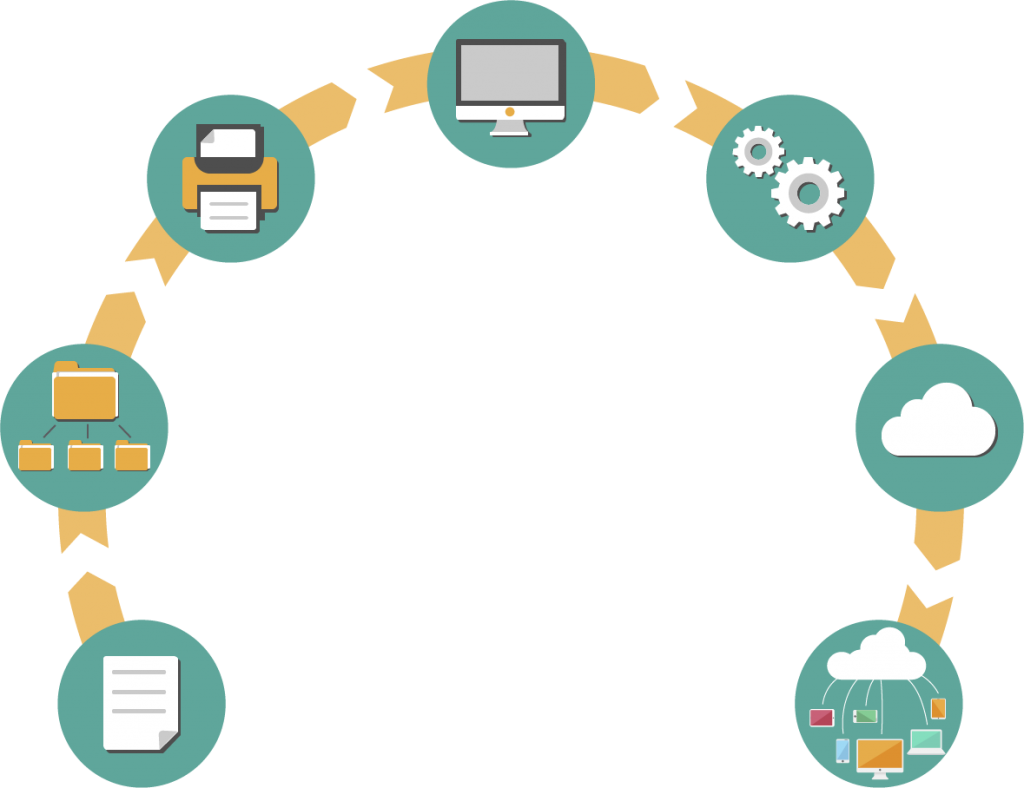
Figure 1.2: Illustration of the paperless process.
Significance of Digitization in Digital Transformation
- Digitization is the foundation: Without digitization, digital transformation cannot occur.
- Digitization generates data: Digital data is an invaluable asset that helps businesses make informed decisions.
- Digitization is the driving force: Digitization promotes innovation and creativity within a business.
- Digitization is the future: The trend of digitization is rapidly growing, and businesses that fail to digitize will fall behind.
Figure 1.3: Eliminating the hassle of paper-based processes and physical storage.
Illustrative Examples
- Digitizing HR records: Instead of storing employee records on paper, businesses switch to electronic HR management systems.
- Digitizing invoices: Instead of issuing paper invoices, businesses switch to electronic invoices.
- Digitizing approval processes: Instead of paper-based approvals, businesses switch to online approvals.
In conclusion, digitization is the first and most important step in digital transformation. It creates a solid foundation for businesses to adopt new technologies, enhance operational efficiency, and strengthen competitiveness.
2. Automation
Automating repetitive processes and tasks is a core element of digital transformation (DX), bringing significant benefits to businesses.

Figure 2.1: Automation in manufacturing.
Figure 2.2: Automation in office work.
The purpose of automation
- Increase efficiency and productivity:
- Replace manual labor: Repetitive, time-consuming tasks are handed over to machines or software, allowing humans to focus on more creative and high-value work.
- Optimize processes: Automation eliminates unnecessary steps, reduces task completion time, and minimizes errors.
- Improve product/service quality:
- Ensure accuracy: Automated machines or software operate according to pre-programmed processes, minimizing human error.
- Increase consistency: Products/services are produced with consistent and stable quality.
- Reduce costs:
- Save labor: Reduces the need to recruit and train employees for repetitive tasks.
- Reduce operating costs: Optimizes the use of energy and resources.
- Enhance competitiveness:
- Quickly adapt to the market: Automation enables businesses to flexibly change production processes to quickly meet market demands.
- Improve customer experience: Customer service is personalized and responded to faster thanks to automated interaction processes.
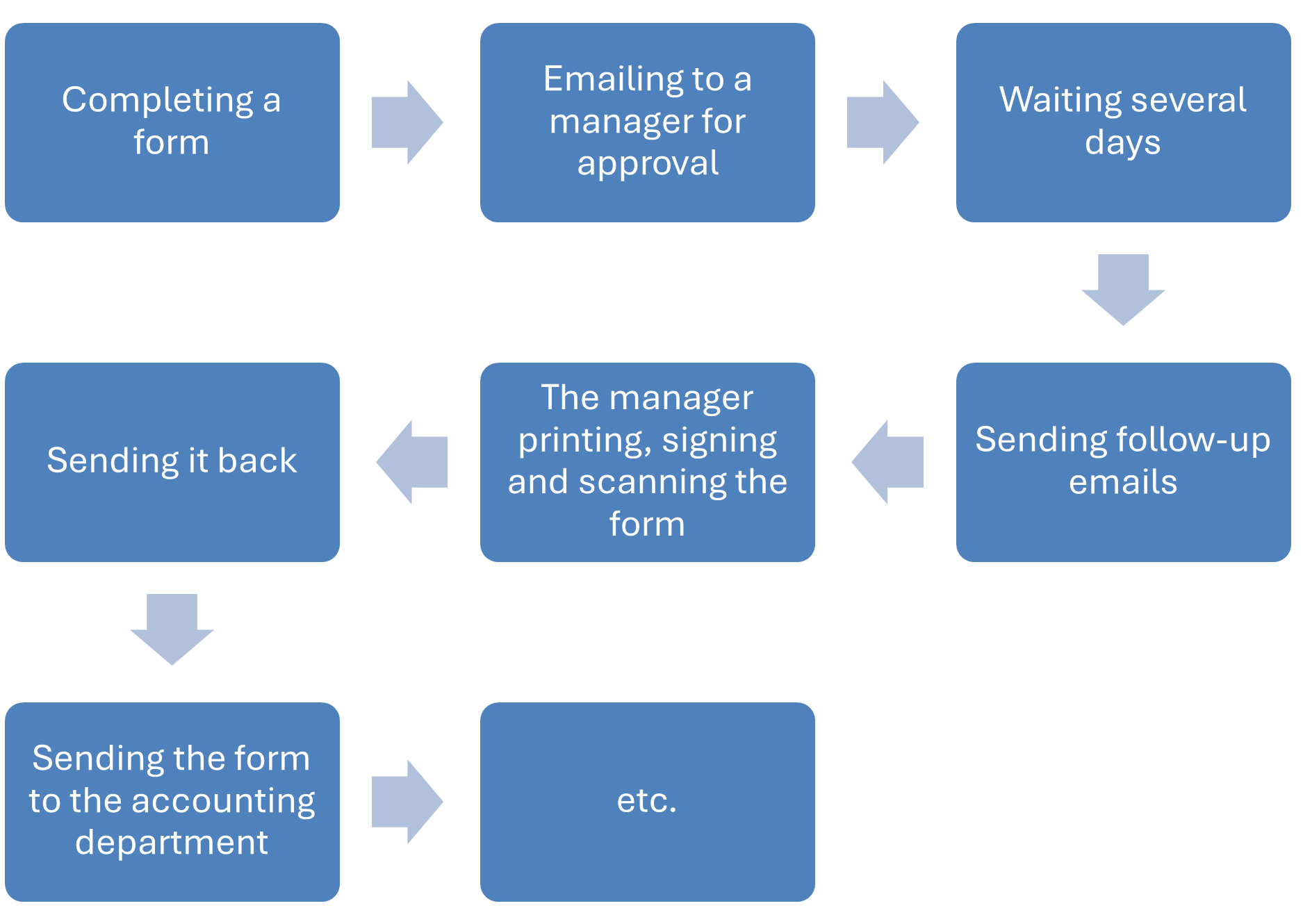
Figure 2.3: Example of a purchasing process
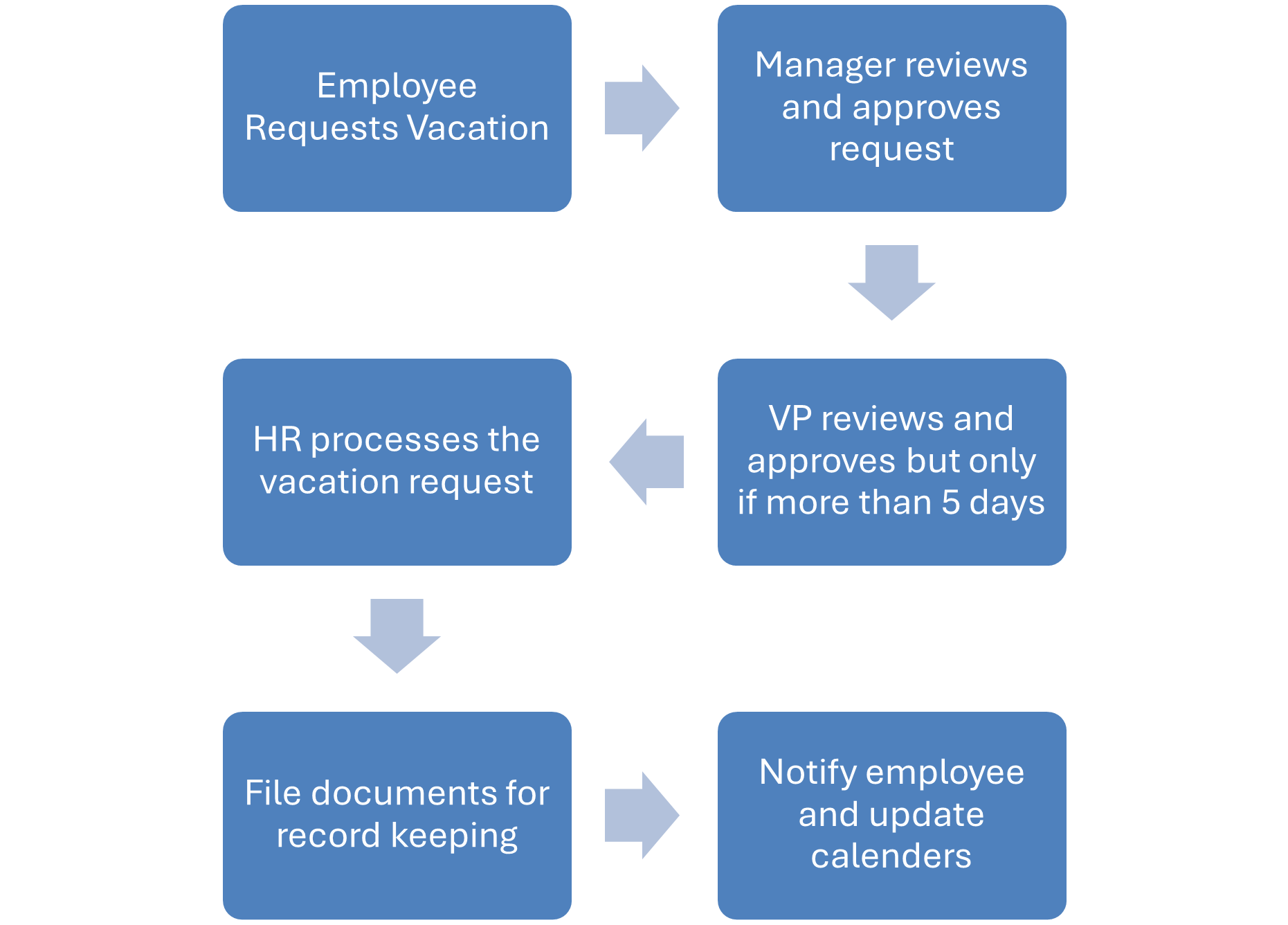
Figure 2.4: Example of a leave request process
The significance of automation in DX
- Driving force for innovation: Automation creates a foundation for businesses to deploy new technologies such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), etc., fostering innovation.
- Changing business models: Automation helps businesses transition from traditional business models to data-driven business models, creating new products/services and distribution channels.
- Opening up development opportunities: Automation helps businesses expand their operations, reach new markets, and create added value.
Figure 2.5: Automation helps create data-driven business models.
Examples of automation
- Manufacturing: Automated production lines, Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) management systems
- Quality control: Measurement equipment management systems, measurement and quality control processes
- Maintenance: Historical incident management systems (Kakotora), preventive maintenance
- Warehouse: Inventory management systems, FIFO management, LOT traceability
- Marketing: Marketing automation, chatbot, email marketing.
- Customer management: CRM (Customer Relationship Management), sales support systems
- Human resources: Human resource management systems, online recruitment

Figure 2.6: Automation - an indispensable aspect of digital transformation
In conclusion, automation is a powerful tool that helps businesses enhance operational efficiency, improve product/service quality, and increase competitiveness in the digital age. Effective application of automation will help businesses succeed in their digital transformation journey.
3. Data Analytics
Data analytics serves as a crucial bridge connecting the vast amounts of data generated during digital transformation and informed business decisions. It empowers businesses to gain deeper insights into customers, markets, and internal operations, ultimately optimizing processes, enhancing operational efficiency, and fostering a competitive edge.

Figure 3.1: Illustration of Data Analytics.
Primary Objectives of Data Analytics in DX
- Understanding Customers:
- Analyzing customer purchasing behavior, preferences, and needs to personalize customer experiences, increase satisfaction, and loyalty.
- Identifying potential customer segments to focus on effective marketing campaigns.
- Optimizing Business Operations:
- Analyzing the performance of marketing, sales, and production campaigns to optimize costs and increase revenue.
- Forecasting market trends and product demand to make timely business decisions.
- Detecting and resolving issues in production and business processes.
- Developing New Products:
- Analyzing market data to identify unmet needs and develop suitable new products.
- Improving Customer Service:
- Analyzing customer feedback to enhance service quality and strengthen customer interactions.
Significance of Data Analytics in DX
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Business decisions are made based on objective, accurate data analysis rather than experience or intuition.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Helps businesses optimize resources, mitigate risks, and increase productivity.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses with effective data analytics capabilities gain deeper insights into markets and customers, enabling them to develop innovative and effective business strategies.
- Innovation and Growth: Data analytics helps businesses identify new opportunities, fostering innovation and sustainable growth.
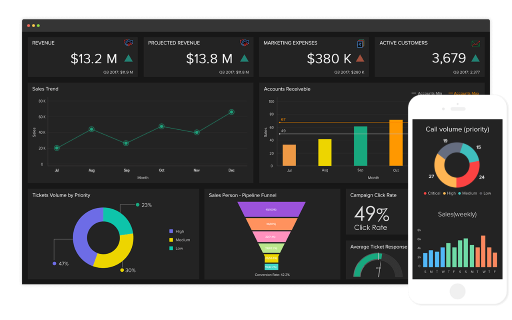
Figure 3.2: Data analytics provides visual representations of information and issues, facilitating quick and accurate decision-making.
Applications of Data Analytics
- Manufacturing: Analyzing product quality, production efficiency, eliminating bottlenecks, and optimizing the supply chain.
- Quality: Assessing trends in dimensional variation, process capability, and conforming product.
- Marketing: Analyzing customer behavior, advertising campaign effectiveness, and building marketing strategies.
- Sales: Analyzing sales team performance, forecasting sales, and managing distribution channels.
- Human Resources: Analyzing employee performance, building training plans, and recruitment.
In conclusion, data analytics is an indispensable tool in the digital transformation journey. It empowers businesses to transition from traditional organizations to data-driven organizations, enhancing competitiveness and achieving sustainable growth.
4. IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT (Internet of Things) s a network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that connect and exchange data. When combined with digital transformation (DX), IoT plays a crucial role in transforming industries and everyday life.

Figure 4.1: IoT as the foundation of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Primary Objectives of IoT in DX
- Enhanced Efficiency: IoT automates processes, optimizes operations, and minimizes errors. For example, in manufacturing, IoT sensors can monitor machine health, predict maintenance, and increase productivity.
- Big Data Collection: IoT generates vast amounts of data from connected devices. This data can be analyzed to make informed business decisions, develop new products, and improve customer service.
- Creating Intelligent Products and Services: IoT enables the creation of intelligent products and services capable of interacting with users and the environment. Examples include smart homes and self-driving cars.
- Enabling New Business Models: IoT creates new business opportunities, such as data-driven services, IoT platforms, and new applications.

Figure 4.2: IoT generates a vast amount of valuable data from connected devices.
Significance of IoT in DX
- Increased Competitiveness: Businesses adopting IoT gain a significant competitive advantage due to higher operational efficiency and innovative products and services.
- Improved Customer Experience: IoT helps create personalized and convenient customer experiences.
- Accelerating Digital Transformation: IoT is a core technology in digital transformation, enabling businesses to transition from traditional to digital business models.
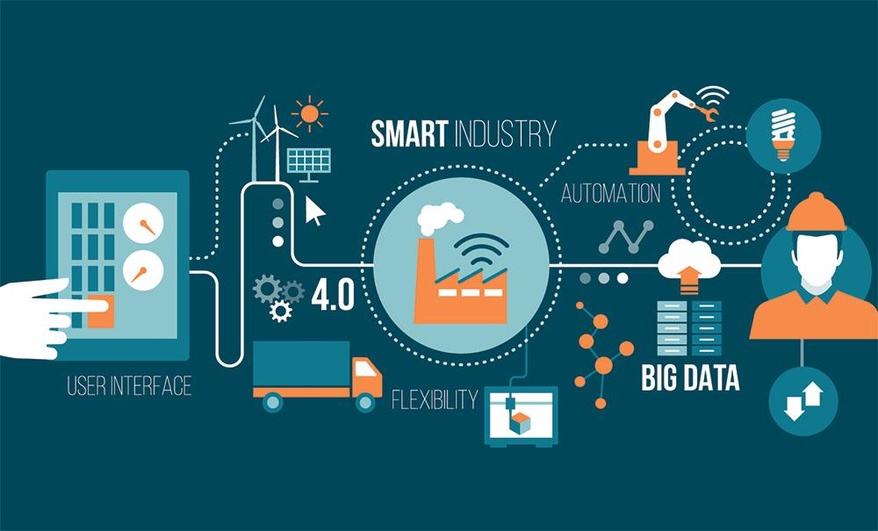
Figure 4.3: Concept of IoT application in a factory.
Examples of IoT Applications
- Manufacturing: Automating production lines, inventory management, predictive maintenance.
- Agriculture: Monitoring soil conditions, weather, automated irrigation, livestock management.
- Healthcare: Personal health monitoring, remote patient monitoring, medical device management.
- Smart Cities: Traffic management, lighting, air quality, waste management.
- Smart Homes: Remote control of lighting, temperature, security, and entertainment.
In conclusion, IoT plays a vital role in digital transformation, offering numerous benefits to businesses and society. Effective IoT implementation will help businesses enhance competitiveness, improve operational efficiency, and create new value.
5. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a transformative technology that has revolutionized how organizations store, manage, and process data. When integrated with Digital Transformation (DX), the cloud plays a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency, scaling businesses, and achieving a competitive edge in the market.
Figure 5.1: Illustration of cloud computing
Purpose of Cloud in Digital Transformation
- Anywhere, Anytime Data Access: The cloud empowers users to access data and applications from any internet-connected device, fostering flexibility and remote work capabilities.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Team members can effectively collaborate on projects, effortlessly sharing documents and information.
- Cost Savings: Instead of investing in expensive servers and hardware, businesses only pay for the cloud services they consume.
- Scalability: The cloud enables businesses to easily scale resources up or down based on actual demand, minimizing overinvestment risks.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud service providers typically invest heavily in security measures to safeguard customer data.
- Innovation: The cloud provides a robust foundation for businesses to develop and deploy new applications, driving innovation.

Figure 5.2: Enhancing data security
Significance of Cloud
- Driving Force for DX: The cloud is a critical tool for organizations to successfully undergo digital transformation. It offers the necessary tools and platforms to digitize business processes and create new products and services.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that effectively leverage cloud benefits gain a significant competitive edge.
- Improved Customer Experience: The cloud enables businesses to deliver better, faster, and more personalized services to customers.
- Business Optimization: The cloud automates many processes, reducing errors and increasing productivity.
Figure 5.3: Serving as a repository and processing center for all digitized data
Cloud Applications in Digital Transformation
- Data Storage: Migrating data to the cloud safeguards it from loss and enhances accessibility.
- Email: Cloud-based email services like Gmail and Outlook offer ample storage and valuable features.
- Virtual Offices: Applications like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 facilitate teamwork, document sharing, and online meetings.
- Data Analytics: Cloud-based data analytics tools empower businesses to extract insights from data for informed decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The cloud provides the computational power required to develop and deploy AI applications.

Figure 5.4: Users can access cloud applications from anywhere.
In Conclusion, The cloud plays a central role in digital transformation. It offers numerous benefits to businesses, from cost savings to enhanced competitiveness. Understanding the purpose and significance of the cloud empowers businesses to make informed decisions regarding its adoption.
6.Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning are playing an increasingly pivotal role in Digital Transformation (DX). Both technologies offer novel capabilities that empower businesses to optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and generate added value.
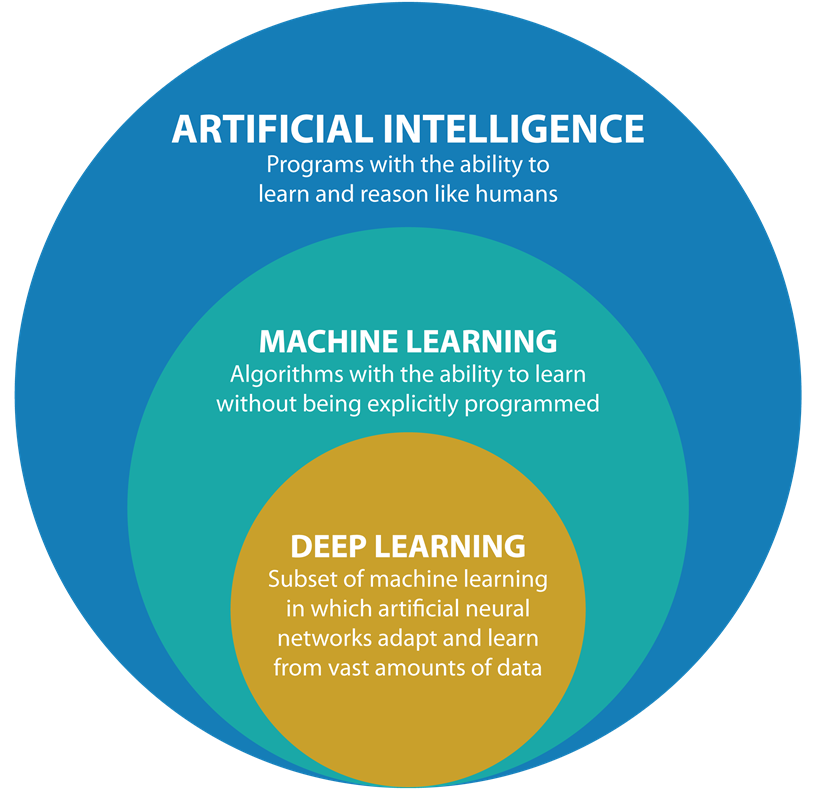
Figure 6.1: Classification of Artificial Intelligence
Figure 6.2: Classification of Machine Learning
Purpose of AI and Machine Learning
- Automation: AI and Machine Learning can automate repetitive tasks, reducing errors and boosting productivity.
- Big Data Analytics: By swiftly and accurately processing large datasets, AI and Machine Learning enable businesses to extract valuable insights and make informed business decisions.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: AI and Machine Learning can be used to personalize customer experiences, provide superior customer service, and anticipate customer needs.
- New Product Development: AI and Machine Learning assist businesses in developing innovative products and services that cater to market demands.
- Operational Optimization: AI and Machine Learning can be applied to optimize production processes, supply chain management, and reduce costs.
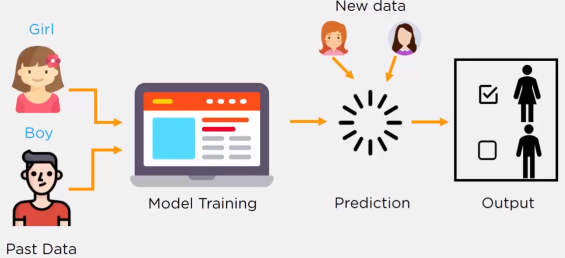
Figure 6.3: A simple illustration of an AI model
Significance of AI and Machine Learning
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses adopting AI and Machine Learning gain a significant competitive edge over those relying on traditional methods.
- New Business Opportunities: AI and Machine Learning create novel business models, products, and services.
- Innovation: AI and Machine Learning drive innovation within organizations, enabling them to adapt swiftly to market changes.
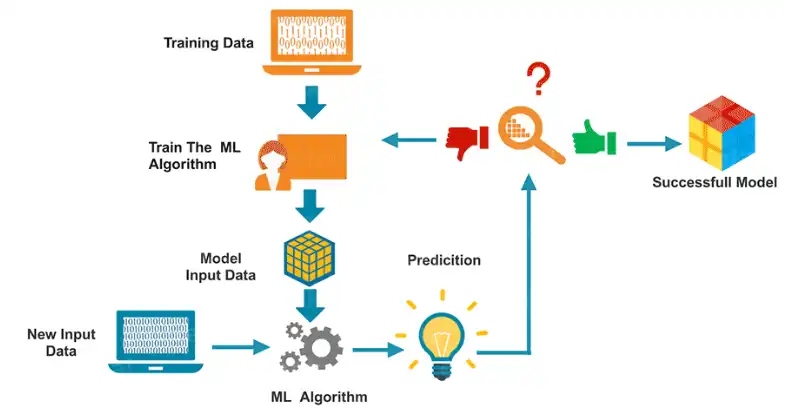
Figure 6.4: How machine learning trains and refines models
Specific Examples
- Manufacturing: AI is used to optimize production processes, ensure product quality, and implement predictive maintenance.
- Retail: AI is employed to recommend products, personalize online shopping experiences, and forecast demand.
- Finance: AI is utilized to detect fraud, assess credit risk, and provide investment advice.
- Healthcare: AI is applied to analyze medical images, detect diseases early, and develop new drugs.
Figure 6.5: Large Language Models (LLMs) and their applications
In conclusion, AI and Machine Learning are instrumental in driving Digital Transformation. They present significant opportunities for businesses to bolster competitiveness, improve operational efficiency, and create new value.